
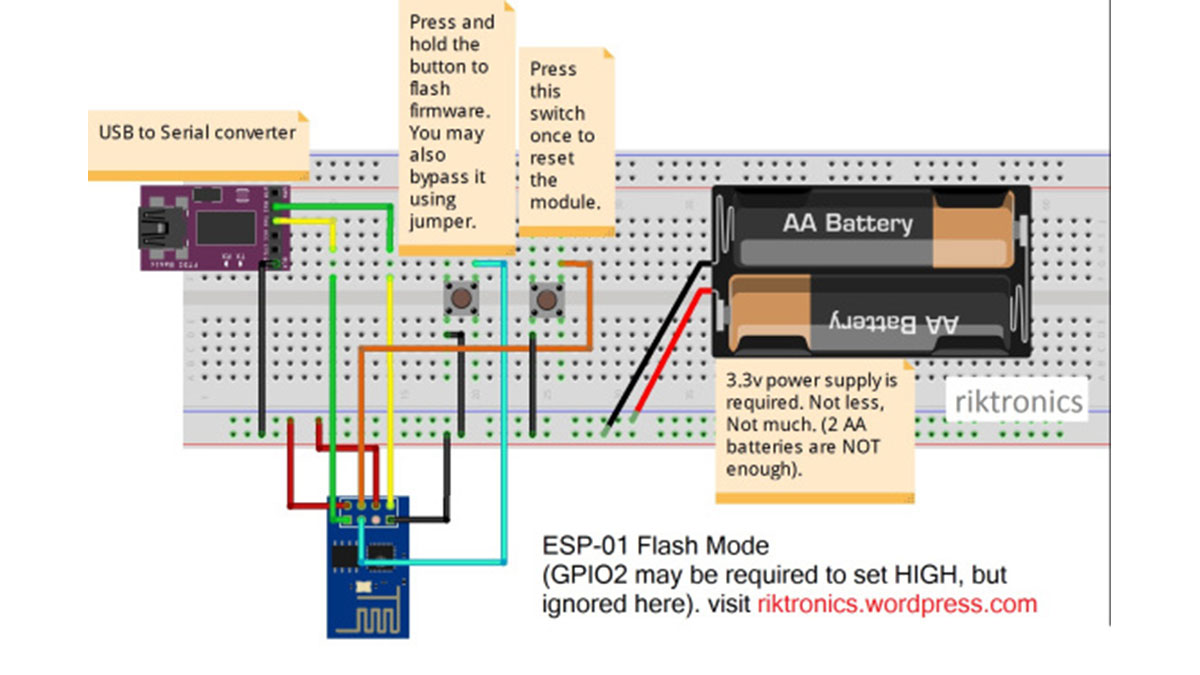
- #ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS INSTALL#
- #ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS SERIAL#
- #ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS FULL#
- #ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS PC#
Remove the modifications made to the ESP shield.
#ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS SERIAL#
Now set the serial monitor speed to 9600 and test again the communication. To set the correct baud rate use this command: I suggest to set the ESP module to use 9600 or 19200 bps. If you are going to use the ESP-01 module with Arduino Uno you have to lower the default baud rate because the SoftwareSerial interface maximum speed is around 38400 bps. The correct settings for the ESP firmware v1.5 are: Test connectivity with 'AT' and 'AT+GMR' commands. Open the Arduino IDE, select the correct COM port and open the serial monitor.

#ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS PC#
#ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS INSTALL#
Sudo pip install -index-url= -r requirements.I have to admit that I had some bad experience when trying to flash new firmwares to my ESP-01 modules but today I have found an easy and reliable way to flash ESP8266 firmware v1.5 (AT v0.51) using my Arduino Uno board as an FTDI controller. esptool.py -port "%_inputname%" write_flash 0x1000 %_foldername%\bootloader.bin 0x10000 %_foldername%\NodeMCU.bin 0x8000 %_foldername%\partitions_singleapp.binĠx1000 nodemcu - firmware - esp32-dir-name\bootloader\bootloader.binĠx10000 nodemcu - firmware - esp32-dir-name\NodeMCU.binĠx8000 nodemcu - firmware - esp32-dir-name\partitions_singleapp.bin Install Python new Version after that "$ pip install esptool"Į.g. Python -m pip install -user -r nodemcu - firmware - esp32-dir-name/sdk/esp32-esp-idf/requirements.txtĠx1000 nodemcu - firmware - esp32-dir-name/build/bootloader/bootloader.binĠx10000 nodemcu - firmware - esp32-dir-name/build/NodeMCU.binĠx8000 nodemcu - firmware - esp32-dir-name/build/partitions_singleapp.binįlash by esptool.py or Config by "make menuconfig" flash after make ** When some package missing, then install and make again ** When Go into menuconfig (Menu), Just Select Exit and let it go ! $ git clone - branch dev - esp32 - recurse - submodules. nodemcu-firmware/app/include/user_modules.hĮsptool.py -chip esp32 -port /dev/ttyUSB0 -baud 115200 -before default_reset -after hard_reset write_flash -z -flash_mode dio -flash_freq 40m -flash_size detectĠx1000 nodemcu-firmware-esp32/build/bootloader/bootloader.binĠx10000 nodemcu-firmware-esp32-2/build/NodeMCU.binĠx8000 nodemcu-firmware-esp32-2/build/partitions_singleapp.binĮsptool.py -port "%_inputname%" write_flash 0x1000 bootloader.bin 0x10000 NodeMCU.bin 0x8000 partitions_singleapp.bin Using your favorite editor (Sublime Text 3 with Vim key bindings thankyouverymuch), open. ** "make" will flash the ESP32 Device after build, So you can confirm the serial port on menuconfig (make menuconfig)Īttached MakeBoot.txt Log file for reference Git pull origin dev-esp32 git submodule init #only if repo was cloned w/o submodules init git submodule update -recursive

Updating your clone from upstream needs an additional command to update the submodules as well:

Versions 3.8.2 and below will produce an incomplete firmware image. GNU make version 4.0 or higher is required for a successful build. The make command initiates the build process, which will start with the configuration menu to set the build options. Git clone - branch dev - esp32 - recurse - submodules. This will fetch the nodemcu repo, checkout the dev-esp32 branch and finally pull all submodules: Run the following command for a new checkout from scratch.
#ESP8266 FIRMWARE UPDATE PROBLEMS FULL#
NodeMCU firmware developers commit or contribute to the project on GitHub and might want to build their own full fledged build environment with the complete tool chain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
